Electric arc fluting fluting caused by electric current roller with electric arc burns adhesive wear on bearing inner ring roller flats adhesive and skidding wear on raceway surface roller end with adhesive wear cage pocket wear from excessive roller movement wear at small ends of cage pocket and on roller bridges scalloping marks in the cup.
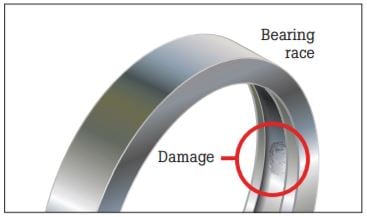
Electric arc bearing damage.
But when noise occurs the damage has usually become substantial enough that failure is imminent.
This electric discharge can occur at very low voltages and may cause severe pitting of the bearing or shaft surfaces or both.
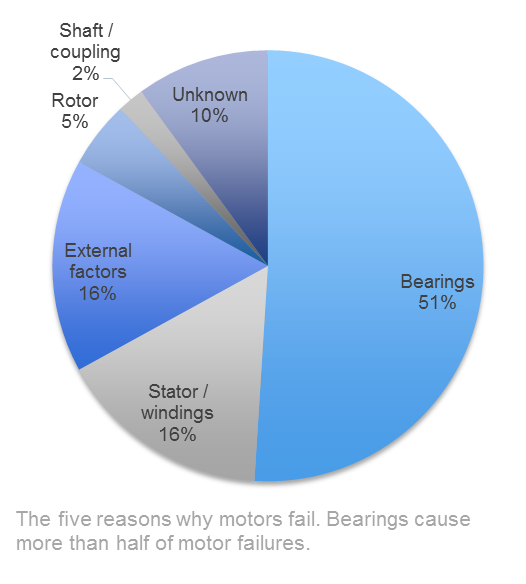
Ball bearings in electric motors support and locate the rotor keep the air gap small and consistent and transfer loads from the shaft to the motor frame.
Arcing can be useful but in some instances unwanted arcing causes damage to industrial structures like bearings.
Improper fit damage electric current damage fluting.
For instance electrical pitting may be present in the linings of bearings where there is insignificant arcing.
In extreme cases damage may occur very rapidly.
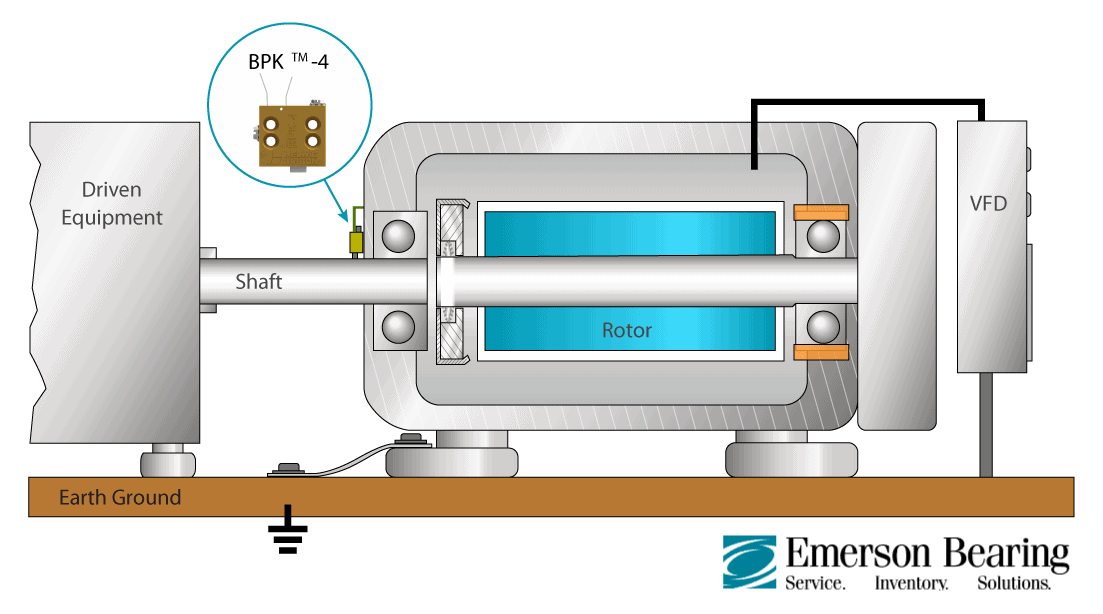
Random electrical currents which come from multiple sources such as wiring insulation static electricity from operating equipment and so on will damage bearings.
The problems isn t just the heat it is the current and the conditions in the bearing that would lead to an arc from ball or roller to the race what we are talking about is small arc strikes on the surface that become much harder than the race or bearing and as it rolls around it causes damage that then destroys the other parts.
Either visible regular patterns flutting or.
W hen bearing fluting or other evidence of electrical damage was clear the cause was frequently believed to be due to some local condition relating to power supply grounding or to a specific vendor or product.
In such a case the pitting may look blackened because of oil deposits.
When it does the cause may be difficult to diagnose as pitting of the bearing surface is followed ultimately by wiping which may obscure the original pitting.
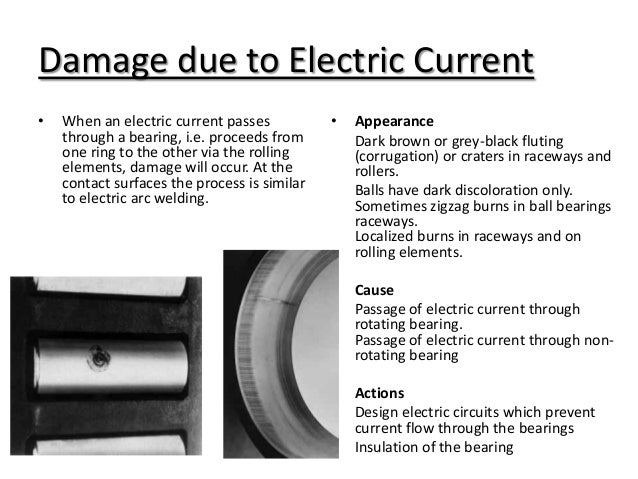
Burns created by improper electric grounding while bearing is stationary.
Series of axial burns caused by electric current passing through the bearing while rotating.
The damage usually appears on the surface of rings and rolling elements and is similar to that produced by electric arc welding.
Once electric arc bearing damage has begun excessive vibrations increased heat increased noise levels and the reduced effectiveness of the lubricant will combine to shorten a bearing s service life.
When a stray current in a machine uses a bearing as its path to ground the resulting damage is referred to as electric arc bearing damage.
The extent of damage to bearings depends upon the amount of energy and its duration.